728x90
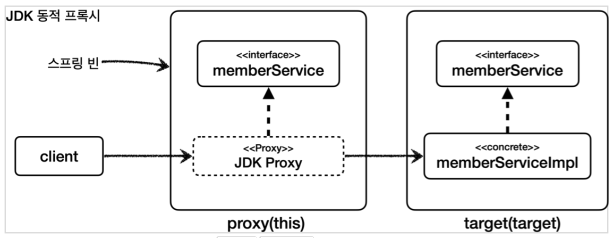
this : 스프링 빈 객체(스프링 AOP 프록시)를 대상으로 하는 조인 포인트
target : Target 객체(스프링 AOP 프록시가 가리키는 실제 대상)를 대상으로 하는 조인 포인트
- this , target 은 다음과 같이 적용 타입 하나를 정확하게 지정해야 한다.
this(hello.aop.member.MemberService)
target(hello.aop.member.MemberService)- * 같은 패턴을 사용할 수 없다.
- 부모 타입을 허용한다
차이점 : 스프링에서 AOP를 적용하면 실제 target 객체 대신에 프록시 객체가 스프링 빈으로 등록된다.
- this는 스프링 빈으로 등록되어 있는 프록시 객체를 대상으로 포인트 컷을 매칭 한다.
- target 은 실제 target 객체를 대상으로 포인트컷을 매칭 한다.
프록시 생성 방식에 따른 차이
스프링은 프록시를 생성할 때 JDK 동적 프록시와 CGLIB를 선택할 수 있다. 둘의 프록시를 생성하는 방식이 다르기 때문에 차이가 발생한다.
JDK 동적 프록시: 인터페이스가 필수이고, 인터페이스를 구현한 프록시 객체를 생성한다.
CGLIB: 인터페이스가 있어도 구체 클래스를 상속받아서 프록시 객체를 생성한다.
MemberService 인터페이스 지정
- this(hello.aop.member.MemberService)
- proxy 객체를 보고 판단한다. this는 부모 타입을 허용하기 때문에 AOP가 적용된다.
- target(hello.aop.member.MemberService)
- target 객체를 보고 판단한다. target 은 부모 타입을 허용하기 때문에 AOP가 적용된다.
MemberServiceImpl 구체 클래스 지정
- this(hello.aop.member.MemberServiceImpl)
- proxy 객체를 보고 판단한다. JDK 동적 프록시로 만들어진 proxy 객체는 MemberService 인터페이스를 기반으로 구현된 새로운 클래스다. 따라서 MemberServiceImpl를 전혀 알지 못하므로 AOP 적용 대상이 아니다.
- target(hello.aop.member.MemberServiceImpl)
- target 객체를 보고 판단한다. target 객체가 MemberServiceImpl 타입이므로 AOP 적용 대상이다

MemberService 인터페이스 지정
- this(hello.aop.member.MemberService)
- proxy 객체를 보고 판단한다. this는 부모 타입을 허용하기 때문에 AOP가 적용된다.
- target(hello.aop.member.MemberService)
- target 객체를 보고 판단한다. target 은 부모 타입을 허용하기 때문에 AOP가 적용된다.
MemberServiceImpl 구체 클래스 지정
- this(hello.aop.member.MemberServiceImpl)
- proxy 객체를 보고 판단한다. CGLIB로 만들어진 proxy 객체는 MemberServiceImpl를 상속받아서 만들었기 때문에 AOP 적용가 적용된다. this 가 부모 타입을 허용하기 때문에 포인트 컷의 대상이 된다.
- target(hello.aop.member.MemberServiceImpl)
- target 객체를 보고 판단한다. target 객체가 MemberServiceImpl 타입이므로 AOP 적용 대상이다
/**
* application.properties
* spring.aop.proxy-target-class=true CGLIB
* spring.aop.proxy-target-class=false JDK 동적 프록시
*/
@Slf4j
@Import(ThisTargetTest.ThisTargetAspect.class)
//@SpringBootTest(properties = "spring.aop.proxy-target-class=false") //JDK 동적 프록시
@SpringBootTest(properties = "spring.aop.proxy-target-class=true") //JDK 동적 프록시
public class ThisTargetTest {
@Autowired
MemberService memberService;
@Test
public void success(){
log.info("memberService Proxy={}", memberService.getClass());
memberService.hello("helloA");
}
@Slf4j
@Aspect
static class ThisTargetAspect{
//부모 타입 허용
@Around("this(hello.aop.member.MemberService)")
public Object doThisInterface(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
log.info("[this-interface] {}", joinPoint.getSignature());
return joinPoint.proceed();
}
@Around("target(hello.aop.member.MemberService)")
public Object doTargetInterface(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
log.info("[target-interface] {}", joinPoint.getSignature());
return joinPoint.proceed();
}
@Around("this(hello.aop.member.MemberServiceImpl)")
public Object doThis(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
log.info("[this-impl] {}", joinPoint.getSignature());
return joinPoint.proceed();
}
@Around("target(hello.aop.member.MemberServiceImpl)")
public Object doTarget(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
log.info("[target-impl] {}", joinPoint.getSignature());
return joinPoint.proceed();
}
}
}
this , target 은 실제 객체를 만들어야 테스트할 수 있다. 테스트에서 스프링 컨테이너를 사용해서 target , proxy 객체를 모두 만들어서 테스트해보자.
- properties = {"spring.aop.proxy-target-class=false"} : application.properties 에 설정하는 대신에 해당 테스트에서만 설정을 임시로 적용한다. 이렇게 하면 각 테스트마다 다른 설정을 손쉽게 적용할 수 있다.
- spring.aop.proxy-target-class=false : 스프링이 AOP 프록시를 생성할 때 JDK 동적 프록시를 우선 생성한다. 물론 인터페이스가 없다면 CGLIB를 사용한다.
- spring.aop.proxy-target-class=true : 스프링이 AOP 프록시를 생성할 때 CGLIB 프록시를 생성한다. 참고로 이 설정을 생략하면 스프링 부트에서 기본으로 CGLIB를 사용한다. 이 부분은 뒤에서 자세히 설명한다.
728x90
'스프링 핵심 원리(고급편)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Ch12. 스프링 AOP(실전 예제) - 재시도 AOP (0) | 2022.04.21 |
|---|---|
| Ch12. 스프링 AOP(실전 예제) - 예제 만들기 & 로그 출력 AOP (0) | 2022.04.21 |
| Ch11. 스프링 AOP(포인트컷) - 매개변수 전달 (0) | 2022.04.20 |
| Ch11. 스프링 AOP(포인트컷) - @annotation, @args, bean (0) | 2022.04.20 |
| Ch11. 스프링 AOP(포인트컷) - @target, @within (0) | 2022.04.20 |